Drugs used in Bronchial Asthma
One logical way of classifying the drugs used in bronchial asthma is on the basis of short term action or long term effect. Thus the Drugs used in bronchial asthma may be short acting or long acting.
SAQ/LAQ/Viva
Classify the drugs used in bronchial asthma with examples.
One way to classify the drugs useful in bronchial asthma, is on the basis of their clinical use in a situation; depending on if a drug is more useful in an acute set-up or for long-term control of asthma.
The drugs which can act on short term basis to produce bronchodilation and be useful in acute set-up to relieve the breathlessness may be viewed as SHORT TERM RELIEVERS.
The drugs which act on long term basis may be called as LONG TERM CONTROLLERS. They produce anti-inflammatory effect, keep the bronchial reactivity low, and prevent the bronchoconstriction in response to noxious stimuli.
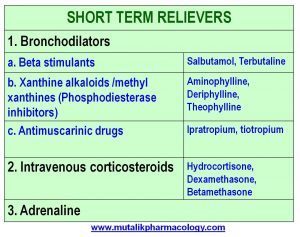

Another way to classify the same drugs is shown below, which is based on the mechanism of action.
1. Bronchodilators
(a) Beta stimulants (Beta agonists): Adrenaline, Ephedrine,
Isoprenaline, Orciprenaline
(b) Selective Beta-2 stimulants:
– Short acting: Salbutamol, Terbutaline, Levosalbutamol,Bitolterol
– Long acting: Salmeterol, Formoterol, Bambuterol, Tulobuterol (Tulobuterol is used as a transdermal patch)
(c) Xanthine alkaloids/methyl xanthines – Aminophylline,
Deriphylline, Theophylline
(d) Antimuscarinic drugs: Ipratropium, Tiotropium
2. Corticosteroids:
(a) Systemic: Hydrocortisone, Dexamethasone, Betamethasone, Prednisone
(b) Inhalational: Beclomethasone, Budesonide, Fluticasone
3. Drugs acting on Leukotrienes:
(a) 5 lipoxygenase inhibitor (Inhibits Leukotriene synthesis): Zileuton
(b) Leukotriene receptor antagonist (Blocker): Montelukast,
Zafirlukast
4. Mast Cell Stabilizers: Cromolyn Sodium (Di-Sodium-Chromoglycate), Nedocromil Sodium
5. Anti-IgE monoclonal antibody: Omalizumab
SAQ/Viva
Explain mechanism of action of Salbutamol.
Salbutamol is a selective Beta-2 agonist (Beta-2 stimulant).
The mechanism of action is described in the following steps.

SAQ/Viva
Explain the mechanism of action of steroids in bronchial asthma/ Explain why steroids are used in the treatment of bronchial asthma.
Steroids act in bronchial asthma by following mechanisms:
- Steroids decrease the hyperreactivity / hyperresponsiveness of the bronchial smooth muscle to the action of bronchoconstricting drugs or stimuli.
- Steroids inhit cyclo-oxygease and thus act as anti-inflammatory.
- Steroids decrease the mucosal edema.
- Steroids decrease the inflammatory cytokines
- Steroids decrease the lymphocytic and eosihophilic infiltration
- They are useful on chronic basis or also in acute emergency to keep the bronchus less reactive.
- Steroids inhibit Phospholipase A2 and reduce the content of histamine and SRS-A in the cells.
SAQ/Viva
Why anti-histamines are not useful in bronchial asthma.
1. It is not only histamine that is released in cases of bronchial asthma. There are other chemical mediators of asthma, on which anti-histamines have no role to play.
2. In severe cases of asthma, the anti-histamines do not achieve a required level in the bronchi; especially when there is severe bronchospasm.
Thanks. Make use of it and revise.
Thank you sir
Thank you so much sir 🙏
Thanks a lot.