Ethyl and Methyl Alcohol
It is important to know how Ethyl and Methyl alcohols get metabolized.
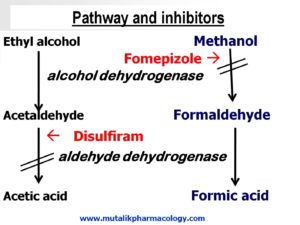
The enzyme that breaks down alcohols is dehydrogenase. It leads to formation of an aldehyde, which further is acted upon by dehydrogenase, to form acid and water.
Ethyl alcohol breaks down into acetaldehyde and acetaldehyde further breaks down by acetaldehyde dehydrogenase (= aldehyde dehydrogenase) into acetic acid.
Methyl alcohol (Methanol) breaks down into formaldehyde, and formaldehyde further breaks down into formic acid.
The products of methanol (Formaldehyde and formic acid) are much more toxic as compared to the products of ethanol (Acetaldehyde and acetic acid). Therefore methanol poisoning is extremely severe, and difficult to treat.
The steps of metabolism of Ethyl alcohol (Ethanol) and Methyl alcohol (Methanol) and inhibitors are shown below.
SAQ/Viva
Mention the principles of acute alcohol intoxication.
Highlights of alcohol intoxication are:
- Hypoglycemia
- Ketosis
Principles of management:
- Gastric lavage to remove if any unabsorbed amount present.
- Tracheal intubation
- Positive pressure ventilation
- Intravenous glucose
- Potassium chloride
- Thiamine 100 mg in 500 ml glucose – Intravenous infusion
- Sodium bicarbonate
- Hemodialysis
SAQ/Viva
Why Disulfiram is used in the management of alcohol addiction?
Disulfiram is an acetaldehyde dehydrogenase inhibitor. When aldohol is consulmed in presence of Disulfiram, Disulfiram will inhibit the conversion of acetaldehyde by inhibiting acetaldehyde dehydrogenase enzyme. So acetaldehyde will accumulate.
Acetaldehyde accumulation leads to an extremely unpleasant feeling comprising of distress and discomfort. (Disulfiram reaction) (Alcohol intolerance). This also includes flusing of face, headache, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, fall in blood pressure (Hypotension), sweating, confusion, and a feeling of severe exhaustion and sleep.
So disulfiram works as aversive therapy, creating a sense of fear of alcohol in the patient’s mind. (Aversion: making the consumption unpleasant).
Hence disulfiram is used in the management of alcohol addiction.
SAQ/Viva
What is Disulfiram-like effect / Antabuse-like effect? Mention the drugs which can produce this, and the clinical implications.
Disulfiram (Also called Antabuse) is used as aversive therapy in the management of alcohol addiction.
Ethyl alcohol is metabolized by alcohol dehydrogenase into acetic acid, and acetic acid is further broken down by the enzyme aldehyde dehydrogenase.
Disulfiram is an aldehyde dehydrogenase inhibitor. It inhibits the breakdwon of acetaldehyde. So if the patient consumes alcohol in presence of Disulfiram, the patient gets a severe unpleasant reaction. This is Disulfiram reaction or alcohol intolerance.
However, there are many drugs who have the same action as that of Disulfiram. So while being on these drugs, if the patient consumes alcohol, the patient gets a similar reaction. Hence this reaction is called Disulfiram-like reaction or Antabuse-like reaction.
Drugs which may produce Disulfiram-like reaction on alcohol consumption:
- Metronidazole, Tinidazole
- Oral antidiabetics like Chlorpropamide
- Cephalosporins: Especially cefoperazone, Cefamandole, Cefotetan, Cefaclor
- H2 blockers: Cimetidine, Ranitidine, Famotidine
- Macrolids: Erythromycin, Roxithromycin, Azithromycin, Clarithromycin
- Sulfa drugs: Sulfonamides, Co-trimoxazole
H2 blockers, macrolids, sulfa drugs