Thyroid hormones and thyroid inhibitors
Watch the video to have the overview.
Hypothalamus secretes TSH-RH (Thyroid stimulating hormone Releasing hormone) (same as TRH/TRF – Thyrotropin Releasing Hormone/Factor), which acts on the pituitary to stimulate the secretion of TSH (Thyroid Stimulating Hormone).
TSH acts on the thyroid gland to secrete T3 and T4.
Thyroid hormones are used to treat hypothyroidism.
Thyroid inhibitors are used to treat hyperthyroidism.
Special Points:
- Propylthiouracil is preferred to carbimazole/methimazole in pregnancy.
- Carbimazole is a prodrug that gets converted to methimazole.
- Fastest acting thyroid inhibitor is Lugol’s Iodine.
- Beta blockers treat the symptoms of hyperthyroidism; they do not affect the thyroid gland function; so they are not called anti-thyroid drugs or thyroid inhibitors
- Antithyroid drug means one which decreases the synthesis of thyroid hormones.
- Thyroid inhibitors include antithyroid drugs and drugs acting by other mechanisms.
LAQ/SAQ/Viva
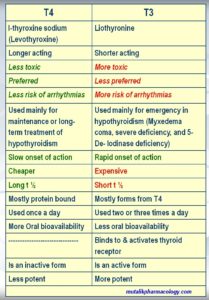
Mention differences between T3 and T4.
Below mentioned are the differences between the two hormones.
T4 (l-thyroxine sodium) is the preferred hormone. It is long acting, andless expensive. It does not lead to sudden severe adverse effects, because its onset of action is slow. Chances of cardiac arrhythmias are less with T4. Its oral bioavailability is better, has a long t 1/2, and can be used on once daily basis, and is preferred for long term treatment of hypothyroidism. It is an inactive form and slowly gets converted into T3.
(Please note) The following table writes T4 in the first column and then T3 in the next column.
SAQ/Viva/LAQ
Mention the uses of thyroid hormones.
Thyroid hormones are important as replacement therapy in the conditions of deficiency of thyroid hormones. In addition, they are useful empirically in other associated conditions.
- Cretinism – sporadic and endemic
- Adult Hypothyroidism (Thyroiditis / Thyroidectomy / Simple goiter with iodine deficiency / Idiopathic hypothyroidism)
- Nontoxic goiter – endemic and sporadic
- Papillary carcinoma of thyroid
- Emergency in hypothyroidism –called myxedema coma – l-thyroxine sodium started as 200-500 mcg Intravenous and continued till oral therapy can be started (or T3 -100 mcg Intravenous to start with and continued as 25 mcg every 6 hours) + Hydrocortisone
- Benign functioning thyroid nodule
- Empirical uses: Include Resistant anemias, Menstrual disturbances, Infertility, Chronic resistant ulcers, and Chronic constipation
SAQ/Viva
Are the thyroid inhibitors same as Antithyroid drugs ? /What is the difference between Antithyroid drugs and thyroid inhibitors?
Thyroid inhibitors is a broad term which means the drugs used to decrease the functional capacity of thyroid gland, and such drugs are used to treat the conditions where there is hyperactive thyroid gland.
Thyroid inhibitors may act by different mechanisms such as –
-decreasing the synthesis of thyroid hormones or
-decreasing the release of thyroid hormones or
-by destroying the thyroid tissue or
-by decreasing the iodide trapping or uptake.
Only those who act by decreasing the synthesis of thyroid hormones are called as Anti Thyroid Drugs. (Examples: Methimazole, Carbimazole, Propylthiouracil)
SAQ/Viva
Classify Thyroid Inhibitors with examples.
Classification of Thyroid Inhibitors
1. Anti-Thyroid Drugs: (Decrease thyroid hormone synthesis)
Examples: Thioamides: Propyl-thiouracil (PTU), Methimazol, Carbimazol
2. Drugs decreasing hormone release:
(a) Iodides: Iodine, NaI, KI
(b) Iodinated contrast media: Ipodate, Ipanoic acid, Diatriazoate
3. Drugs destroying thyroid tissue (radioactive iodine)131-I, 125-I, 123-I
4. Drugs decreasing iodide trapping/uptake (Ionic Inhibitors) SCN Thiocynate), ClO4 (Perchlorate), NO3 (Nitrate)
SAQ/LAQ/Viva
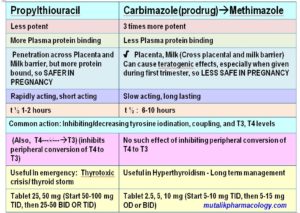
Mention the differences between Propylthiouracil (PTU) and Carbimazole/Methimazole.
Carbimazole is a prodrug that gets converted to methimazole. This group of drugs is generally slow acting and long acting, and is preferred for long-term management of hyperthyroidism. This inhibits the iodination of tyrosine residues, coupling, and decreases the levels of T3 and T4.
Propylthiouracil does have the above action, but in addition can inhibit the peripheral conversion of T4 to T3, and hence can produce rapid, dramatic effect. It is rapidly acting and acts for short time, and hence it is preferred in emergency management of hyperthyroidism, which is known as thyyroid storm.
The differences between the two groups of drugs are shown below in the form of a table.
SAQ/Viva
Mention adverse effects of Anti-thyroid drugs.
Antithyroid drugs means the drugs which decrease the synthesis of thyroid hormones. They are carbimazole/methimazole and propylthiouracil.
Because the antithyroid drugs decrease the functional capacity of the thyroid gland to secrete T3 and T4, the most obvious adverse effect of Anti-thyroid drugs is HYPOTHYROIDISM. In addition, there are more adverse effects as listed below:
- Hypothyroidism
- GI, skin rash (maculopapular rash), fever
- Alopecia, graying of hair
- Liver damage
- Agranulocytosis, hypoprothrombinemia
- Teratogenicity is likely with carbimazole/methimazole especially when given during the first trimester of pregnancy. Propylthiouracil is comparatively safer.
SAQ/Viva
Why propylthiouracil (PTU) is preferred to carbimazole/methimazole for use during pregnancy?
Propylthiouracil as well as Carbimazole/Methimazole both cross the placental barrier; howerver, propylthiouracil is extensively bound to the plasma proteins. Hence the teratogenic effects are less likely with propylthiouracil.
Carbimazole/Methimazole is more likely to produce teratogenic effects especially during the first trimester of pregnancy.
Propylthiouracil is less likely to produce teratogenic effects, and hence is safer.
So propylthiouracil is preferred to carbimazole/methimazole for use during pregnancy.
SAQ/Viva
Why beta blockers are useful in treatment of hyperthyroidism?
Beta blockers – (examples – propranolol, atenolol, metoprolol, nadolol) are useful in treatment of hyperthyroidism by following mechanisms:
- Beta blockers block the sympathetic stimulation by the excess thyroid hormones. Thus they produce pr9mpt relief from the symptoms of sympathetic overactivity. (They control the symptoms of tachycardia and palpitation. They control the increased contractility and automaticity of the heart. They decrease the blood pressure. They prevent the chances of cardiac arrhythmias).
- Beta blockcrs have some additional action of inhibiting 5′ deiodinase and thus preventing peripheral conversion of T4 to T3 to some extent. Thus they help to control the hyperthyroidism.
Beta blockers do not have any effect on the thyroid gland function.
SAQ/Viva
What is Lugol’s Iodine? Mention its actions and uses.
Lugol’s Iodine means 5% iodine in 10% potassium iodide or sodium iodide
It can be used by oral route of administration as syrup in the dose of 5 to 15 drops per day or tablets or also by intravenous route.
Actions:
1. It is a thyroid inhibitor and acts by decreasing the thyroid hormone release.
It is the fastest acting thyroid inhibitor, and reaches its peak action in 10-15 days.
2. It makes the thyroid gland shrink in size.
3. It makes the thyroid gland firm, less fragile, and less vascular.
Uses:
- Pre-operative preparation for thyroidectomy (start at least 15 days prior to surgery)
- Can be used in THYROID STORM (fast acting) (NaI or KI – IV or oral to stop further release of T3, T4)
- For prophylaxis of endemic goiter as Iodized salt.
- NaI and KI are used as EXPECTORANTS.
- Tincture iodine is used as antiseptic.
Hello It is mentioned almost everywhere. Some topics may be in the process of updating. Thanks for pointing out.