Hypolipidemic Drugs
Hypolipidemic Drugs or Drugs used for Hyperlipidemia /Dyslipidemia are useful to keep cholesterol levels in control over a long period of time.
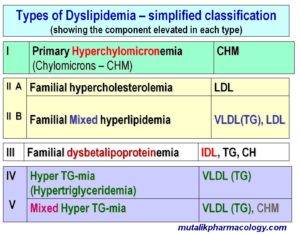
Here is the simplified classification of dyslipidemias; where it shows which component is elevated in each type.
[LDL: low-density-lipoprotein cholesterol; VLDL: Very low density lipoprotein cholesterol; TG: Triglycerides; CHM: Chylomicrons; IDL: Intermediate density lipoprotein cholesterol]
Based on the mechanism of action and the action of hypolipidemic drugs, the following table describes each drug group is mainly useful in which type of dyslipidemia.
| N | Drug/Drug group | Used for which type of dyslipidemia |
| 1 |
Statins |
All types of dyslipidemia |
|
2 |
Ezetimibe (Used with statins) |
All types of dyslipidemia |
|
3 |
Fibrates |
Hypertriglyceridemia |
|
4 |
Niacin |
All types of dyslipidemia |
| 5 | Resins (Not commonly used) (Contraindicated in hypertriglyceridemia) | LDL hypercholesterolemia |
SAQ/Viva
Classify the drugs used for hyperlipidemia according to their mechanism of action and site of action.
The following table describes the various drug groups as per their mechanism and site of action.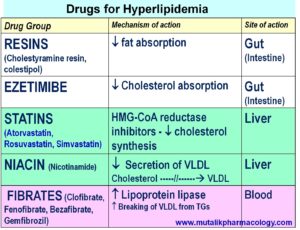
SAQ/LAQ/Viva
Classify hypolipidemic drugs with examples.

SAQ/LAQ/Viva
Mention adverse effects of hypolipidemic drugs.
See the following table. It also mentions precautions for each drug/drug group.
| N | Drug group | Adverse effects/Precautions/Contraindications |
| 1 | Statins |
1. Myopathy: (10% cases): Increase creatine kinase release from skeletal muscles, muscle spasm, pain, tenderness; (increased risk of myopathy, if used with fibrates or niacin) 2. Increased aminotransferases enzymes especially in pre-existing liver disease 3. Headche, nausea, skin rashes, bowel upset 4. Teratogenic effects 5. Can’t be used in pregnancy, lactation 6. Can’t be used in children, teenagers 7. Resins decrease statin absorption. (Give statins 1 hour before or 4 hours after resins) |
| 2 | Ezetimibe |
1. GI distress, abdominal pain, diarrhea 2. Fatigue,tiredness 3. Back pain, arthralgia, tingling, numbness, cough 4. Liver dysfunction |
| 3 | Resins |
1. Bloating, constipation, gritty and unpleasant taste, flatulence 2. Decreased absorption of statins (Give statins 1 hour before or 4 hours after resins) 3. Decreased absorption of Vitamin A, D, E, K, Folate 4. Decreased absorption of digoxin, thiazide diuretics, warfarin |
| 4 | Fibrates |
1. Cholelithiasis (cholesterol gallstones) – Due to increased biliary cholesterol excretion 2. Myopathy: Muscle weakness, tenderness – More if fibrates are used with statins 3. GI disturbances, nausea 4. Skin rashes 5. Leukopenia, decreased hematocrit 6. Pancreatitis / carcinogenicity 7. Can’t be used in pregnancy/lactation/hepatic-renal dysfunction, gallbladder disease 8. Displace anticoagulants, antidiabetics from plasma proteins, and exaggerate their effect |
| 5 | Niacin |
1. Flushing, sense of warmth (Vasodilation), increased heat production, increased PG release – Give NSAIDs to prevent this 2. Nausea, vomiting, abdominal discomfort 3. Skin rashes, pruritus, dry skin (Acanthosis) 4. Moderate increase in liver enzymes, hepatotoxicity, cholestatic jaundice 5. Hyperglycemia 6. Hyperuricemia, joint pains/swelling 7. Myopathy – muscle weakness 8. Can’t be used in pregnancy |
SAQ/Viva
Why statins are advised to be taken at bedtime?
Statins inhibit cholesterol synthesis.
Statins are competitive inhibitors of the enzyme – 3-hydroxy-3 -methyl-glutaryl coenzyme A reductase. (HMG coA reductase inhibitors). By inhibiting this enzyme, they decrease conversion of HMG coA to mevalonic acid, which is the rate limiting step in cholesterol synthesis.
The activity of HMG coA reductase enzyme is highest at midnight; and Most of the statins (except Atorvastatin and Rosuvastatin) are short acting (Half life 1-4 hours).
So, if a statin is consumed during the day, by the time the HMG coA reductase enzyme is at peak levels, the concentration of the statin is likely to be much less. Therefore most of the statins are advised to be taken at bedtime, so that they shall produce maximum effect by inhibiting the HMG coA reductase activity that is highest at midnight.
This rule does not apply to Atorvastatin and Rosuvastatin, because both of them are long acting (Half life of 18-24 hours)
SAQ/Viva
Mention the additional benefits of statins. (other than lowering cholesterol).
-
Increased nitric oxide production (endothelial cells)
-
Improved coronary artery compliance
-
Stabilization of plaque
-
Preventing the chances of plaque rupture
-
Anti-atherosclerotic action
-
Decreased risk of coronary events & mortality
-
Anti-inflammatory effect (Decrease the macrophage-mediated inflammation)
-
Reduced chances of thrombus formation
- Secondary prevention of myocardial infarction and stroke in patients with symptomatic atherosclerotic disease (angina or transient ischemic attacks)
- Primary prevention of myocardial infarction and stroke in high-risk patients
-
Antioxidant properties (Atorvastatin)