Drugs used in Diarrhea
Diarrhea is increased frequency of passing stools. It also involves poorly formed stools.
Most of the diarrheas may be self limiting.
The treatment of diarrhea involves 3 types of management.
- Specific: To treat the cause
- Supportive:
- Rehydration – Fluid and electrolyte replacement: Oral (Oral Rehydration Solution) (ORS) and/or Intravenous rehydration as required
- Nutrition
- Managing shock
- Managing acidosis
- Pro-biotics: Micro-organisms (To allow growth of the microflora): Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG, Saccharomyces boulardii, Bifidobacterium bifidum,Bacillus coagulans, and a yeast – Saccharomyces boulardi
- Symptomatic / Nonspecific:
- Anti-motility drugs (To decrease the frequency of passing stools): Loperamide, Diphenoxylate-Atropine combination
- Gastro-Intestinal Protectives and Adsorbents: Methyl cellulose, Bismuth subcarbonate/salicylate
- Anti-secretory agents: Racecadotril, Atropine, Octreotide, Sulfasalazine, Mesalazine
SAQ/Viva
Mention the importance and advantages of using Oral Rehydration Therapy (ORT).
Oral Rehydration Therapy (ORT) means supplying electrolytes and glucose by oral route of administration.
1. ORT is one of the least expensive therapies to manage diarrhea.
2. The solution can be prepared in a simplest way anywhere.
3. Plain water available at home and the component substances from local market can be used to prepare Oral Rehydration Solution.
4. No specialist doctors or experts are needed for administration of fluid.
5. The solution need not be sterile.
6. Healthcare workers, family members or even non-professionals can administer oral rehydration solution.
7. Despite the presence of vomiting, if the patient continues ORS treatment, it is able to correct the vomiting caused by acidosis.
8. Addition of glucose to the fluid is helpful to accelerate the absorption of sodium and water by the small intestine.
9. Mild to moderate dehydration and acidosis gets corrected by ORT within 4 to 6 hours.
SAQ/Viva
Why anti-motility agents are contraindicated in Acute Infective Diarrhea?
When there is increased frequency of stools, the pathogenic organisms responsible for acute infective diarrhea are cleared out from the intestines due to increased intestinal motility.
In this situation, if anti-motility agents are used, they markedly decrease the intestinal motility, and decrease the passage/clearance of pathogens from intestines !!
So if there are invasive organisms involved, they get trappped, and they remain in the intestines.
To prevent this, anti-motility agents are contraindicated in Acute Infective Diarrhea.
SAQ/Viva
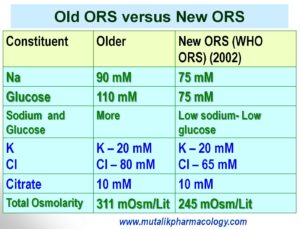
Mention the differences between the older ORS and the New ORS formula by WHO.
SAQ/LAQ/Viva
Mention the advantages of using the new WHO formula-ORS (Modified ORS).
The highlight of the new formula ORS (Oral Rehydration Solution), suggested by WHO in 2002 (Modified ORS) is – it is a low-glucose, low-sodium, low osmolarity formula.
The advantages of using this new formula ORS:
1. The efficacy of the ORS is found to be improved with glucose and sodium both kept at 75mM and the low value of osmolarity.
2. Maximum water absorption takes place if the glucose concentration is lower. (in the range of 60-110 mM). If the glucose concentration is increased, then the glucose appears in stools and increases the stool volume.
3. Maximum water absorption; because of the slightly hypotonic solution.
4. Due to the new formula, the need for IV Supplementation decreases by 33%.
6. The stool volume is significantly reduced (by about 20%).
7. Incidence of vomiting reduces by about 30%
Thank you so much sir🙏