Fluoroquinolones
Fluoroquinolones mainly act against gram negative organisms. In patients of young age, they can produce damage to articular cartilage, tendonitis and tendon rupture.
Special Points:
- Fluoroquinolones are obtained from synthetic source.
- Fluoroquinolones are bactericidal. They bind to two nuclear enzymes involved in DNA replication: 1. DNA gyrase (Topoisomerase II) (mainly in gram negative organisms), 2. Topoisomerase IV (mainly in gram positive organisms)
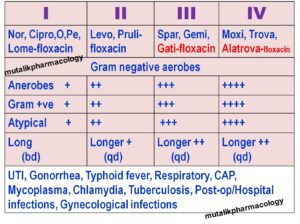
- Levofloxacin, Gemifloxacin, Gatifloxacin, Moxifloxacin are sometimes called RESPIRATORY FLUOROQUINOLONES.
Some important adverse effects of fluoroquinolones:
- Fluoroquinolones chelate positive ions like Calcium, magnesium, aluminium, iron, zinc – so never ingest with food or drugs containing these positive ions – examples – milk, milk products, antacids, hematinics, iron supplements etc.
- Fluoroquinolones affect the collagen metabolism and chondrogenesis – hence – Tendonitis, Tendon rupture -Rupture and Erosion of Articular cartilage, and Arthropathy – more effect on weightbearing joints in growing children – also old individuals are susceptible to arthropathy.
- Fluoroquinolones do have an adverse effect on CNS – Confusion, hallucinations, insomnia, dizziness, headache, SEIZURES
- Gatifloxacin – Hyper/hypoglycemia,
- Trova, Alatrovafloxacin – Hepatotoxicity
- Gatifloxacin, Sparfloxacin – QT Prolongation, Arrhythmias
- Enzyme inhibition – CP450 enzymes – Inhibition of breakdown of certain drugs and their excess effect and toxicity – example – warfarin – bleeding
- Hemolysis in G6PD deficient patients – bleeding
- Phototoxicity – Lome, Pe, Spar, Gatifloxacin
A video session shall give you a broad overview.
SAQ/LAQ/Viva
Mention uses of fluoroquinolones
- Urinary tract and genital infections (except moxifloxacin), (Norfloxacin 400 bid oral) Gonorrhea (ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin, single dose treatment), gonococcal cervicitis, Chlamydial urethritis, cervicitis, prostatitis, Chancroid
- Upper –lower respiratory infections – Sinusitis, bronchitis, streptococcal infections, CAP, Chlamydia, Mycoplasma, Legionella (levo, gati, gemi, moxi) (respiratory fluoroquinolones
- Typhoid fever (ciprofloxacin 750 bid x 10 days)
- Postoperative, nosocomial (hospital-acquired)infections
- Bacterial diarrhea – Salmonella, Shigella, E coli, Campylobacter
- Intraabdominal, pelvic, gynecologic infections
- Bones, joints, skin, soft tissue, Eye infections
- Anthrax with RMP/ampi/clinda/clarithro
- Tuberculosis MDR, XDR, atypical – MAC (Levo – 500 od, Ofloxacin, Cipro, Moxi)
- Leprosy (Ofloxacin) (100-200 bid – oral, iv)
- Meningeal infections (Peflox 400 bid oral, i.v.) (Ö CNS)
- Prophylaxis – meningococcal carrier state, neutropenia
- Infections in Patients with Cystic fibrosis, diabetic foot..
Fluoroquinolones – Classification, Examples, Spectrum, Uses