Anti-Anginal Drugs
I advise you to go through the two videos to have overview of the topic of antianginal drugs.
Angina is chest pain due to ischemia.
The anti-anginal drugs may be used –-as an emergency to relieve the pain or -used prophylactically (to prevent the attacks of angina)
Two distinct varieties of angina are shown below: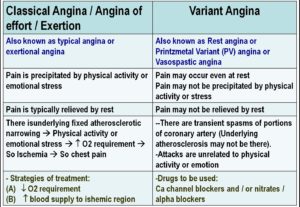
SAQ/Viva
Explain the rationale for use of Nitrates in Acute Attack of Angina.
Nitrates produce vasodilation. (Relaxation of smooth muscle of the blood vessels).
(They release Nitric oxide (NO) in the Smooth muscle, which stimulates guanylate cyclase which converts GTP into cyclic GMP (cGMP). So there is dephosphorylation of myosin light chain, and hence smooth muscle relaxation).
Nitrates dilate capacitance vessels (venules) more predominantly than resistance vessels (arterioles).
Venodilation leads to peripheral pooling of the blood.
So there is dereased preload as well as end-diastolic pressure.
This decreases the O2 requirement of the heart and thus relieves isehemia, and the chest pain.
They also produce favorable redistribution of the blood to the ischemic areas by dilation of large epicardial coronary arteries.
Thus the anginal chest pain is relieved.
(Nitrates are not analgesic drugs !! They produce vasodilation, decrease the work of the heart, relieve ischemia, and thus relieve chest pain).
SAQ/LAQ/Viva
Mention the therapeutic uses and adverse effects of Nitrates.
Smooth muscle relaxation is the main action of nitrates. Most of the therapeutic uses are based on this action.
- Acute attack of angina – Nitroglycerine or Isosorbide Dinitrate by sublingual route
- Chronic prophylaxis of angina – Oral / Slow release preparations of various nitrates. May be combined with beta blockers
- Hypertensive crisis – Nitroglycerine by intravenous route
- Biliary colic
- Esophageal Spasm
- Cyanide Poisoning: NaNo2 (Sodium Nitrite)
Adverse Effects of Nitrates:
- Reflex Tachycardia, Palpitation, flushing, throbbing headache
- Hypotension
- Dizziness, Postural hypotension, Syncope
- Tolerance
- Methemoglobinemia
- Monday disease – Industrial exposure to inhalational nitrites producing vasodilation and headache, which gradually decreases on daily exposure, and disappears on the weekends, and reappears on re-exposure after the wash-out period.
- Precipiation of severe hypotension on exposure to Sildenafil/Tadalafil (drugs used for erectile dysfunction): Additive effect due to accumulation of cyclic GMP (cGMP)
SAQ/LAQ/Viva
Explain: Why nitrates are combined with Beta Blockers for chronic prophylaxis of angina?
(A)
1. Nitrates produce reflex tachycardia, and it is compensated by Beta Blockers.
2. Beta blockers may lead to ventricular dilatation over a long period of time, and this is compensated by nitrates.
(B)
- Beta blockers and nitrates have synergistic actions, so addition of beta blockers decreases the dose requirement of nitrates.
- Because the nitrates are needed in lower doses, their dose-related toxicity is minimized.
- Now since nitrates can be started in lower doses from the beginning, there is more range available to increase their doses (as may be needed due to the phenomenon of tolerance). Thus addition of Beta Blockers helps to delay the tolerance to nitrates.
Due to the above advantages, nitrates are combined with Beta Blockers for chronic prophylaxis of angina.
These notes really helped me in revising right before my preliminary exams, and I could write the exam confidently! Thank you!
Thanks a lot. Keep it up, Siddhant. All the best.